1:28 understand how to carry out calculations involving amount of substance, relative atomic mass (Aᵣ) and relative formula mass (Mᵣ)
The following formula allows for the interconversion between a mass in grams and a number of moles for a given substance:
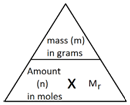
Example 1:
Calculate the amount, in moles, of 8.8 g of carbon dioxide (CO2).
Step 1: Calculate the relative formula mass (Mr) of carbon dioxide (CO2).
Step 2: Use the formula to calculate the amount in moles.
Example 2:
Calculate the mass of 2 mol of copper(II) sulfate (CuSO4).
Step 1: Calculate the relative formula mass (Mr) of copper(II) sulfate (CuSO4).
Step 2: Rearrange the formula to calculate the mass.