2:16 understand how metals can be arranged in a reactivity series based on their displacement reactions between: metals and metal oxides, metals and aqueous solutions of metal salts
A metal will displace another metal from its oxide that is lower in the reactivity series. For example, a reaction with magnesium and copper (II) oxide will result in the magnesium displacing the copper from its oxide:
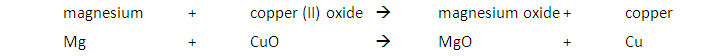
A metal will also displace another metal from its salt that is lower in the reactivity series. For example, the reaction between zinc and copper (II) sulfate solution will result in zinc displacing the copper from its salt:
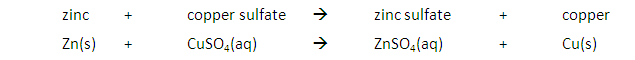
The blue colour of the copper (II) sulfate solution fades as colourless zinc sulfate solution is formed.