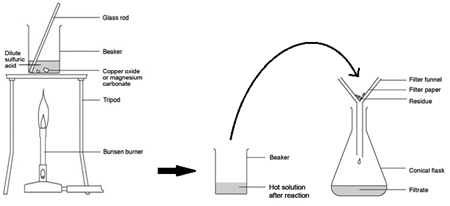
2:42 practical: prepare a sample of pure, dry hydrated copper(II) sulfate crystals starting from copper(II) oxide
Excess Solid Method:
Preparing pure dry crystals of copper sulfate (CuSO4) from copper oxide (CuO) and sulfuric acid (H2SO4)
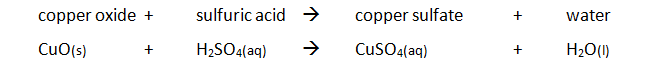
| Step | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Heat acid (H2SO4) in a beaker | Speeds up the rate of reaction |
| Add base (CuO) until in excess (no more copper oxide dissolves) and stir with glass rod | Neutralises all the acid |
| Filter the mixture using filter paper and funnel | Removes any excess copper oxide |
| Gently heat the filtered solution (CuSO4) | To evaporate some of the water |
| until crystals form on a glass rod | Shows a hot saturated solution formed |
| Allow the solution to cool so that hydrated crystals form | Copper sulfate less soluble in cold solution |
| Remove the crystals by filtration | Removes crystals |
| Dry by leaving in a warm place | Evaporates the water |