2:44a describe tests for these gases: hydrogen, carbon dioxide
Test for hydrogen gas (H2)
- Test: use a lit splint
- Result: burns with a squeaky pop
Test for carbon dioxide (CO2)
- Test: bubble through limewater
- Result: limewater turns cloudy
https://www.allnetwork.org/kontak/
Test for hydrogen gas (H2)
Test for carbon dioxide (CO2)
Tests for gases
| Gas | Test | Result if gas present |
|---|---|---|
| hydrogen (H2) | Use a lit splint | Gas pops |
| oxygen (O2) | Use a glowing splint | Glowing splint relights |
| carbon dioxide (CO2) | Bubble the gas through limewater | Limewater turns cloudy |
| ammonia (NH3) | Use red litmus paper | Turns damp red litmus paper blue |
| chlorine (Cl2) | Use damp litmus paper | Turns damp litmus paper white (bleaches) |
A flame test is used to show the presence of certain metal ions (cations) in a compound.
Properties of the platinum or nichrome wire is:
When put into a roaring bunsen burner flame on a nichrome wire, compounds containing certain cations will give specific colours as follows.
| Ion | Colour in flame test |
|---|---|
| lithium (Li⁺) | red |
| sodium (Na⁺) | yellow |
| potassium (K⁺) | lilac |
| calcium (Ca²⁺) | orange-red |
| copper (II) (Cu²⁺) | blue-green |

Describe tests for the cations Cu2+, Fe2+ and Fe3+, using sodium hydroxide solution
First, add sodium hydroxide (NaOH), then observe the colour:

Describe tests for anions: Carbonate ions (CO32-)
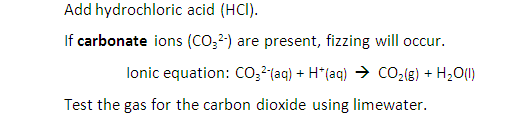
Describe tests for anions: Halide ions (Cl–, Br– and I–)
Underneath are the tests for:
chloride ion test, bromide ion test, iodide ion test, sulfate ion test, carbonate ion test

Describe tests for anions: Sulfate ions (SO42–)

Describe tests for anions: Carbonate ions (CO32-)
Add anhydrous copper (II) sulfate (CuSO4) to a sample.
If water is present the anhydrous copper (II) sulfate will change from white to blue.
If the sample is pure water it will boil at 100oC