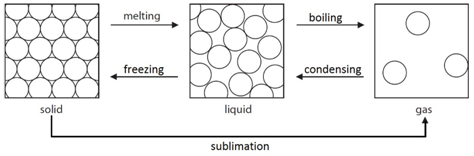
Melting: When a solid is heated, the energy makes the particles vibrate fast enough so that the forces of attraction between the particles break. For example H2O(s) –> H2O(l)
Freezing: When a liquid is cooled, the particles move slow enough so that the forces of attraction between them will hold them into a solid. For example H2O(l) –> H2O(s)
Boiling: When a liquid is heated strongly, the energy makes the particles move fast enough so that all forces of attraction are broken. For example H2O(l) –> H2O(g)
Condensing: When a gas is cooled, the particles move slow enough so that the forces of attraction between them will hold them as a liquid. For example H2O(g) –> H2O(l)
Sublimation: A small number of substances have the ability to change directly from a solid to a gas when heated. For example CO2(s) –> CO2(g)