3:07 (Triple only) use bond energies to calculate the enthalpy change during a chemical reaction
Each type of chemical bond has a particular bond energy. The bond energy can vary slightly depending what compound the bond is in, therefore average bond energies are used to calculate the change in heat (enthalpy change, ΔH) of a reaction.
Example: dehydration of ethanol
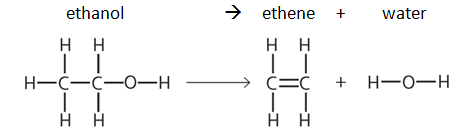
Note: bond energy tables will always be given in the exam, e.g:
| Bond | Average bond energy in kJ/mol |
|---|---|
| H-C | 412 |
| C-C | 348 |
| O-H | 463 |
| C-O | 360 |
| C=C | 612 |
So the enthalpy change in this example can be calculated as follows:
| Breaking bonds | Making bonds | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Bonds | Energy (kJ/mol) | Bonds | Energy (kJ/mol) |
| H-C x 5 | (412 x 5) = 2060 | C-H x 4 | (412 x 4) = 1648 |
| C-C | 348 | C=C | 612 |
| C-O | 360 | O-H x 2 | (463 x 2) = 926 |
| O-H | 463 | ||
| Energy needed to break all the bonds | 3231 | Energy released to make all the new bonds | 3186 |
Enthalpy change, ΔH = Energy needed to break all the bonds - Energy released to make all the new bonds ΔH = 3231 – 3186 = +45 kJ/mol (ΔH is positive so the reaction is endothermic) |
|||