2.01 use the following units: ampere (A), coulomb (C), joule (J), ohm (Ω), second (s), volt (V) and watt (W)
unit for:
current : Ampere (A)
charge : coulomb (C)
resistance : ohm (Ω)
time : second (s)
potential difference : volt (V)
power : watt (W)
https://www.allnetwork.org/kontak/
unit for:
current : Ampere (A)
charge : coulomb (C)
resistance : ohm (Ω)
time : second (s)
potential difference : volt (V)
power : watt (W)
Fuses Stop the flow of current by melting if the current is too high. So protecting sensitive components and people because if the components function at too higher temperature it can cause a fire.
Circuit breakers again break the circuit if current is too high.
Insulation and double insulation prevent people from touching exposed wires and getting shocks.
Earthing provides a low resistance path to the earth so if some one does come into contact with a current instead of flowing through them to the earth giving them a shock it flows through the earthing wire.
|
Resistance causes transfer of electrical energy to heat energy. Some components are designed to have a high resistance to make sure this happens, for example electrical heaters that have lots of resistors to ensure a high resistance so a lot of heat is produced. |
power (w) = current (A) x voltage (V)
when looking at a circuit a component will be given a power and a voltage appropriate to run at then the current can be calculated so the rating of the fuse can be selected for slightly higher than that.
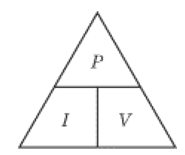
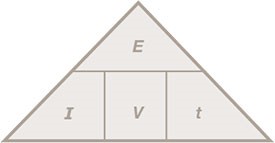
Energy (J) = potential difference (V) x current (A) x Time (s)
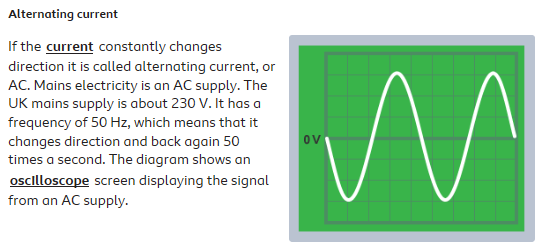
AC is constantly changing magnitude and direction. AC is how mains electricity is produced from turbines.
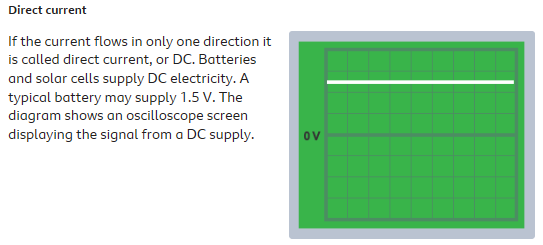
DC is constant. And is produced from a battery and used in some sensitive components like in computing.
Advantages of parallel circuits:
Advantages of series circuits:
Notes on current:
in the bellow diagram the red box could represent a wire, a bulb, a resistor or a diode.
By changing the resistance of the variable resistor the graphs are reproduced.
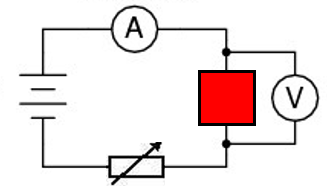
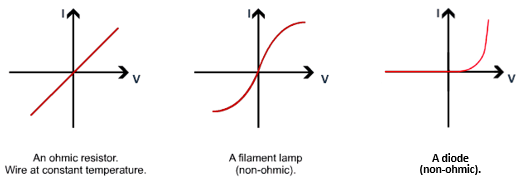
Since V = IR, as you increase the resistance in a circuit, the current will decrease.
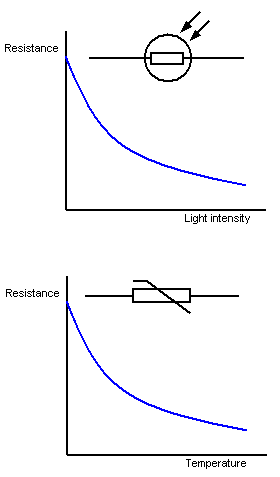
LDR
As illumination increases, resistance decreases
Thermistor
As temperature increases, resistance decreases.
A lamp can be added to a circuit to check for a current. If current is flowing, the lamp will light up.
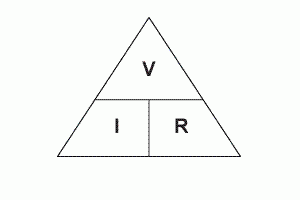
Potential difference (V) = Current (A) x Resistance (Ω)
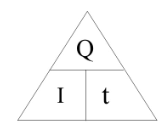
current is rate of flow of charge so I=Q/t
Charge (C) = Current (A) x Time (s)
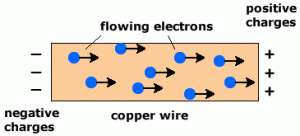
Electrons are negatively charged and free to flow in a metal so carry charge
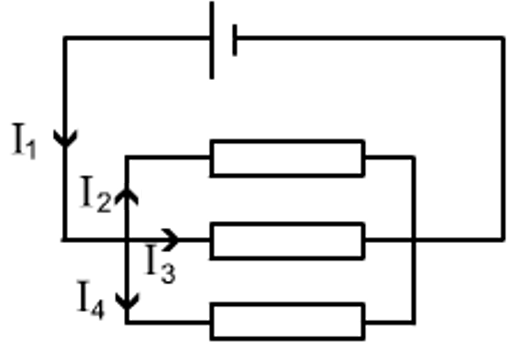
At a junction current ‘splits’ to take both paths.
It comes back together when the paths meet again.
I1 = I2 + I3 +I4
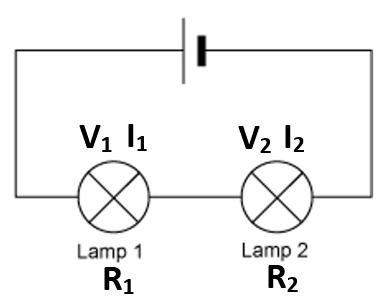
VT = V1 + V2
IT = I1 = I2
RT = R1 + R2
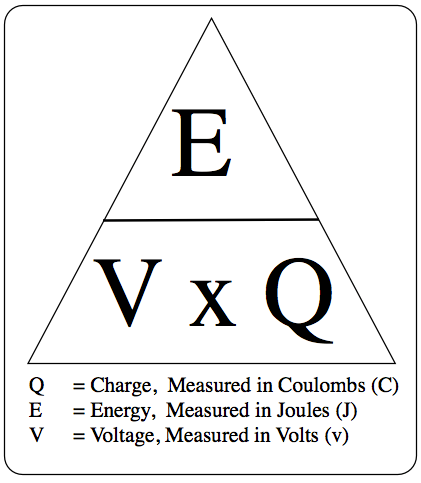
Energy Transferred (J) = charge (C) x Voltage (V)
Conducting Materials:
Will conduct electricity
Insulating Materials:
Will not conduct electricity
|
Paper is charged negatively in certain regions. Then positively charged paint droplets are sprayed onto the paper and attracted to the negative regions of the paper giving the desired image. |