4:32 (Triple only) know that ethanol can be manufactured by: 1) reacting ethene with steam in the presence of a phosphoric acid catalyst at a temperature of about 300⁰C and a pressure of about 60–70atm; and 2) the fermentation of glucose, in the absence of air, at an optimum temperature of about 30⁰C and using the enzymes in yeast
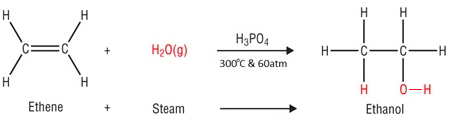 In the hydration of ethene, ethanol is made by passing ethene and steam over a catalyst.
In the hydration of ethene, ethanol is made by passing ethene and steam over a catalyst.
Water is added to ethene, this is known as hydration.
Conditions
Catalyst: Phosphoric acid (H3PO4)
Temperature: 300°C
Pressure: 60 atm
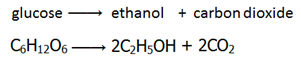 Fermentation is the conversion of sugar, e.g. glucose into ethanol by enzymes from yeast.
Fermentation is the conversion of sugar, e.g. glucose into ethanol by enzymes from yeast.
Conditions
Catalyst: Zymase (enzyme found in yeast)
Temperature: 30°C – The process is carried out at low temperatures as not to denature the enzymes.
Other: Anaerobic (no oxygen present) – if oxygen were present, the yeast produce carbon dioxide and water instead of ethanol.